Sample Exam
Question 1

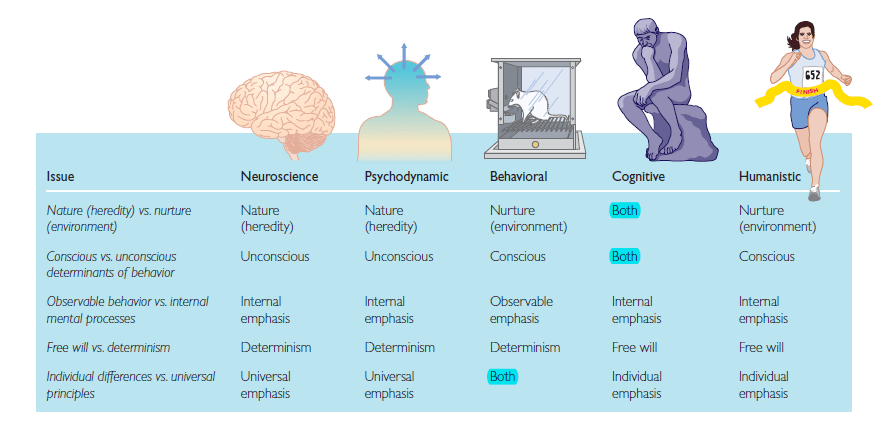
- Biological: genes, neurotransmitters
- Behavioral: external stimuli, environment, Pavlov's dog, learned and unlearned behaviors
- Psychodynamic: Sigmund Freud, childhood, id, ego, superego, projective test
- Cognitive: attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, thinking
- Humanistic: free will, self-actualization, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, inherently good
Question 3

- Hermann Ebbinghaus: forgetting curve, memory, learning curve
- Hermann von Helmholtz: founder of experimental psychology
- William James: first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States, natural selection, functionalism
- Wilhelm Wundt: one of the founders of psychology, opened the Institute for Experimental Psychology at the University of Leipzig in Germany in 1879
- John Locke: a continuity of consciousness
Question 4

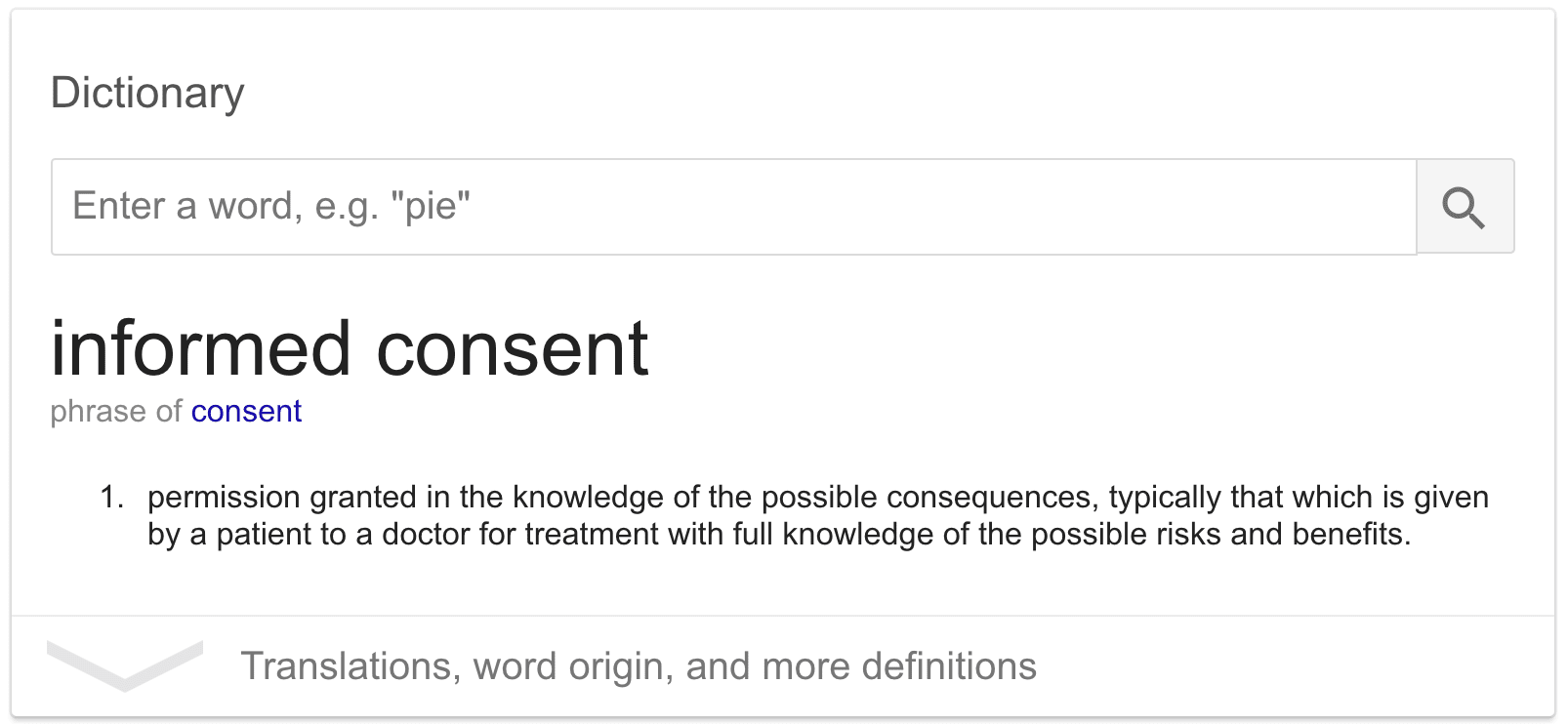

- "Duty to inform" is a term used in law.
Question 5

- An operational definition is a description of how we will measure our variables, and it is important in allowing others understand exactly how and what a researcher measures in a particular experiment.
Question 7

- When a neuron is at rest, the neuron maintains an electrical polarization
- (i.e., a negative electrical potential exists inside the neuron's membrane with respect to the outside).
- This difference in electrical potential or voltage is known as the resting potential.
- At rest, this potential is around -70mV.
Question 8


Question 10


Question 11
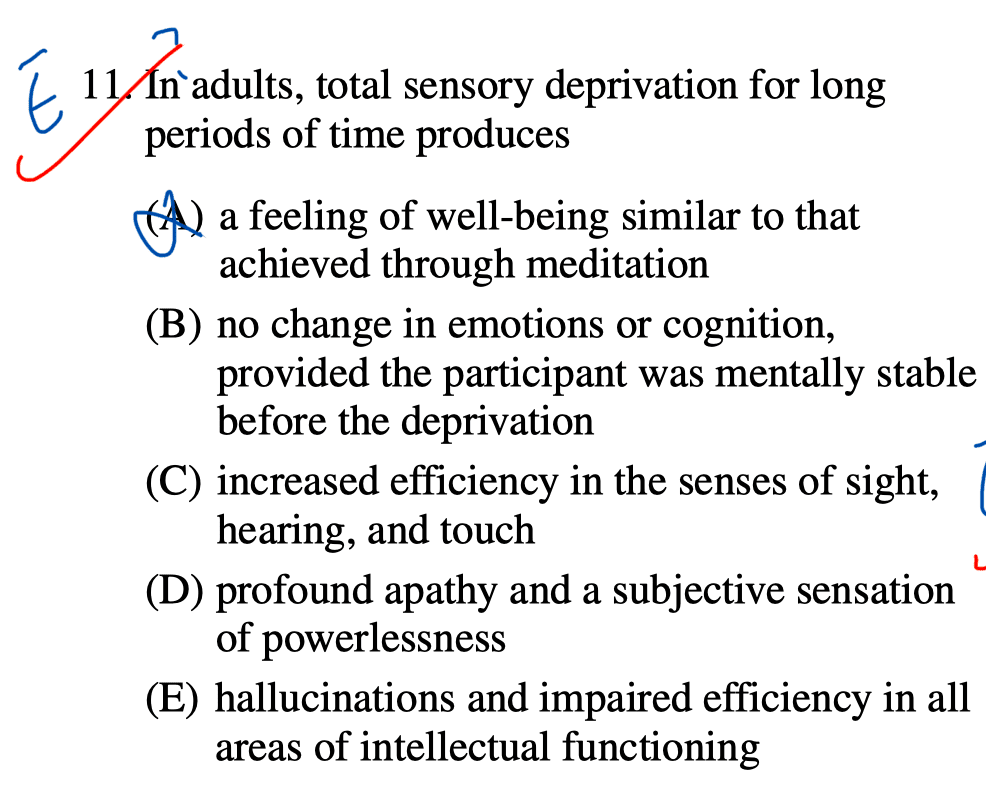

Question 13

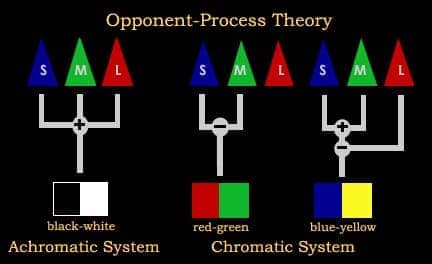


Question 17

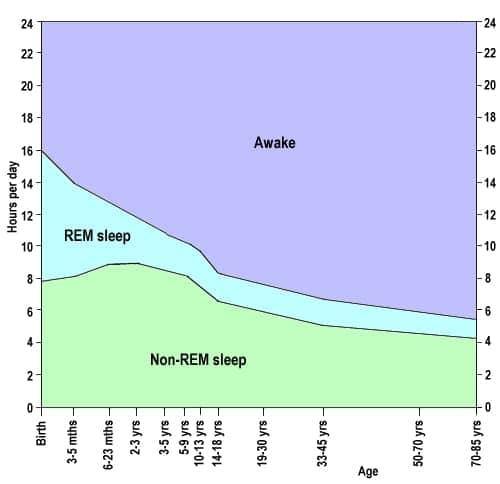
Question 18


Question 20

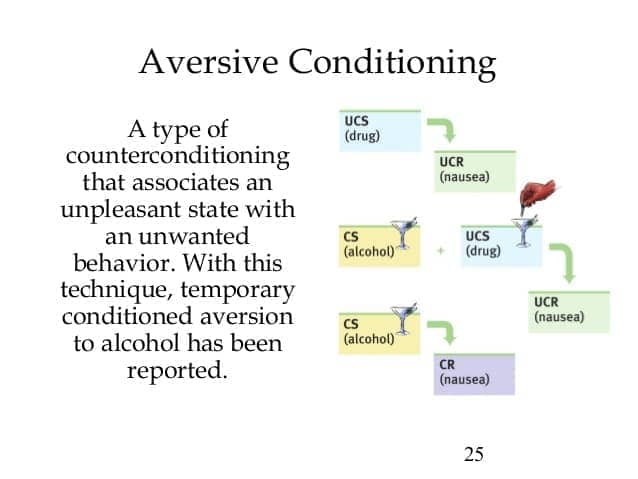
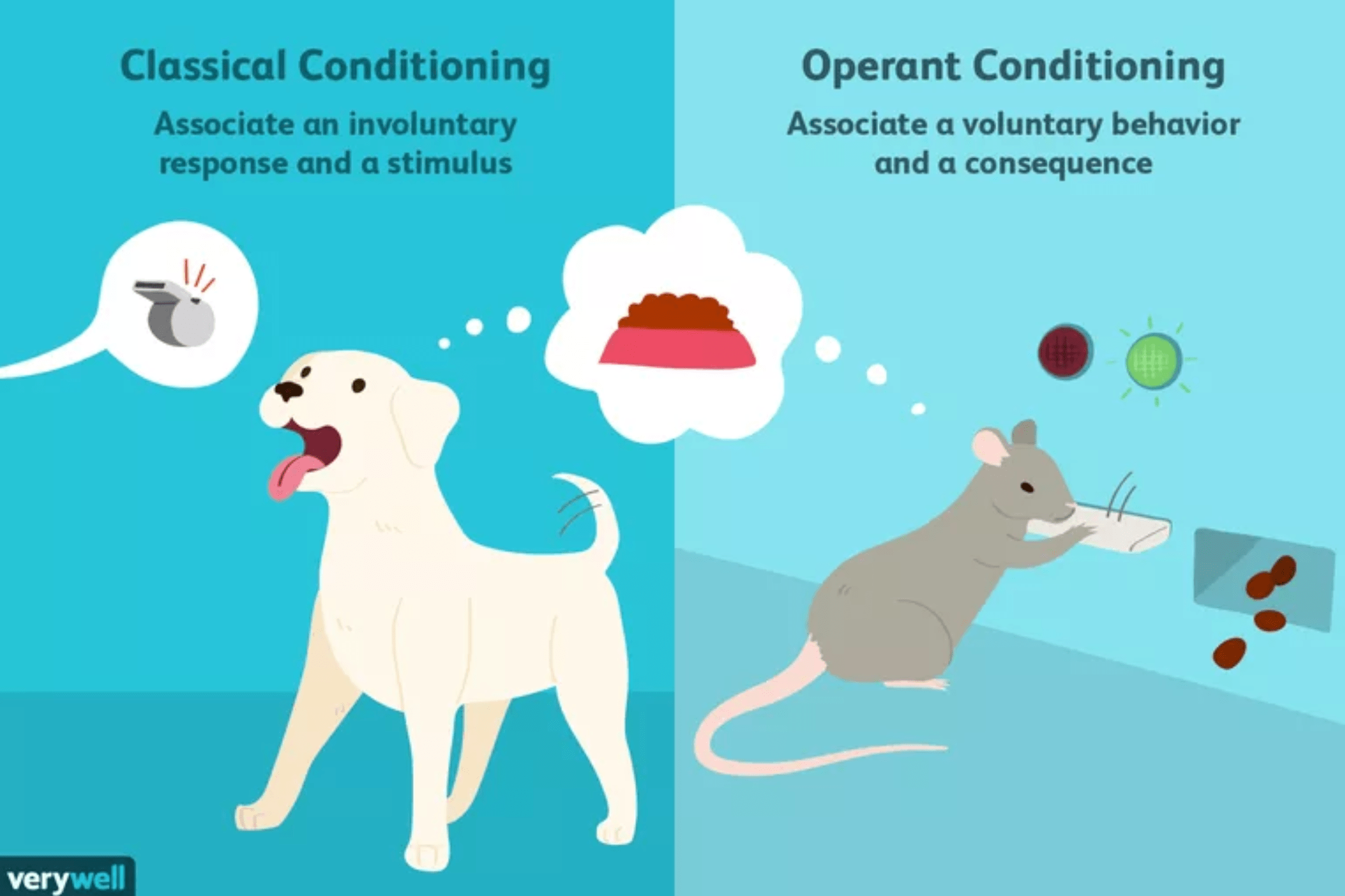
Question 23


- Primary Reinforcer: An innately reinforcing stimulus like food or drink
- Secondary Reinforcer: A learned reinforcer that gets its reinforcing power through association with the primary reinforcer
Question 25

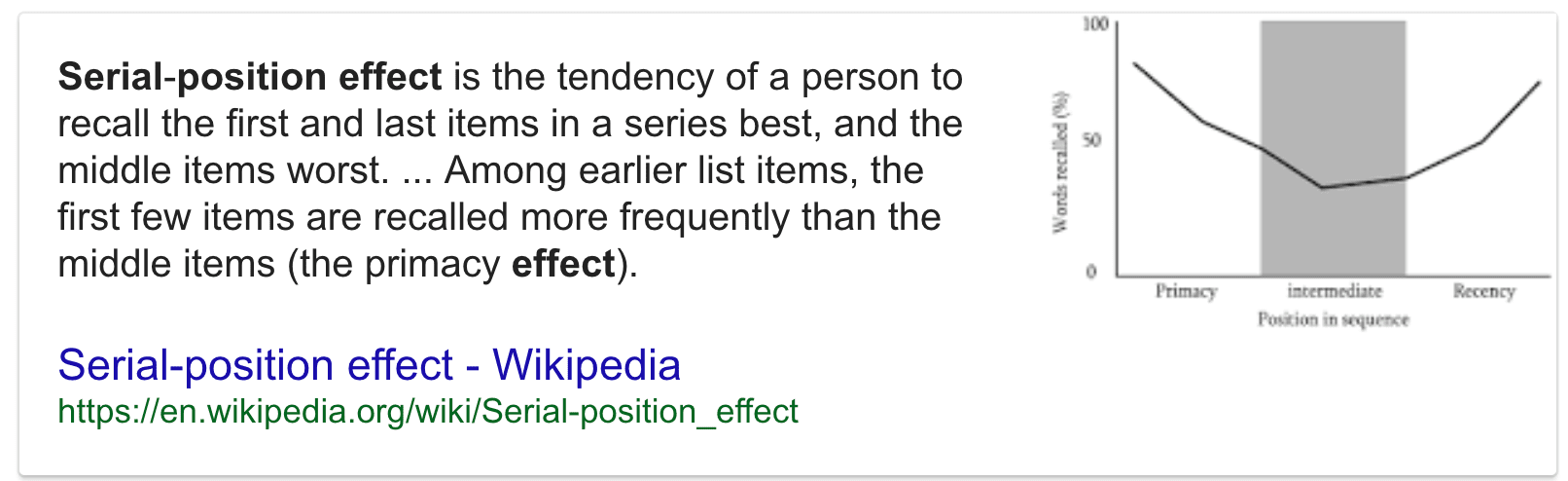
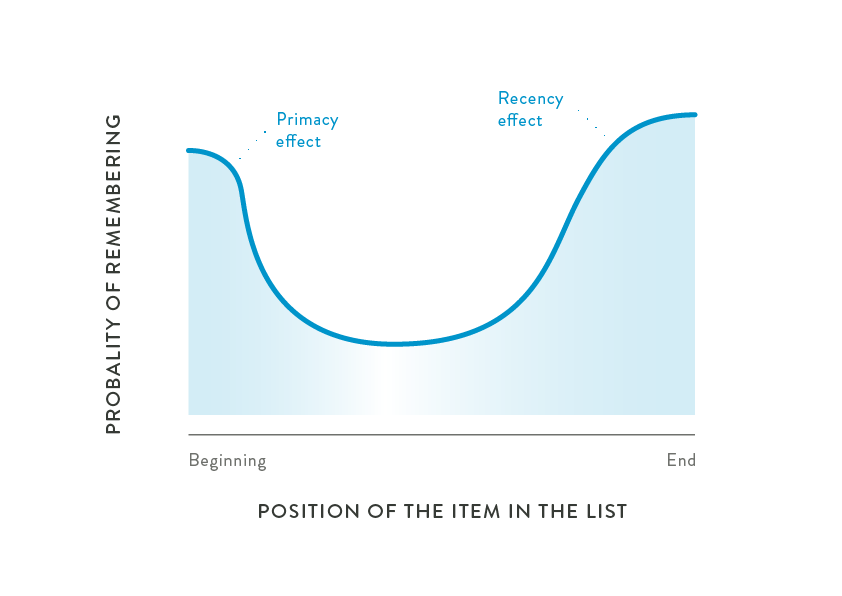
Question 26


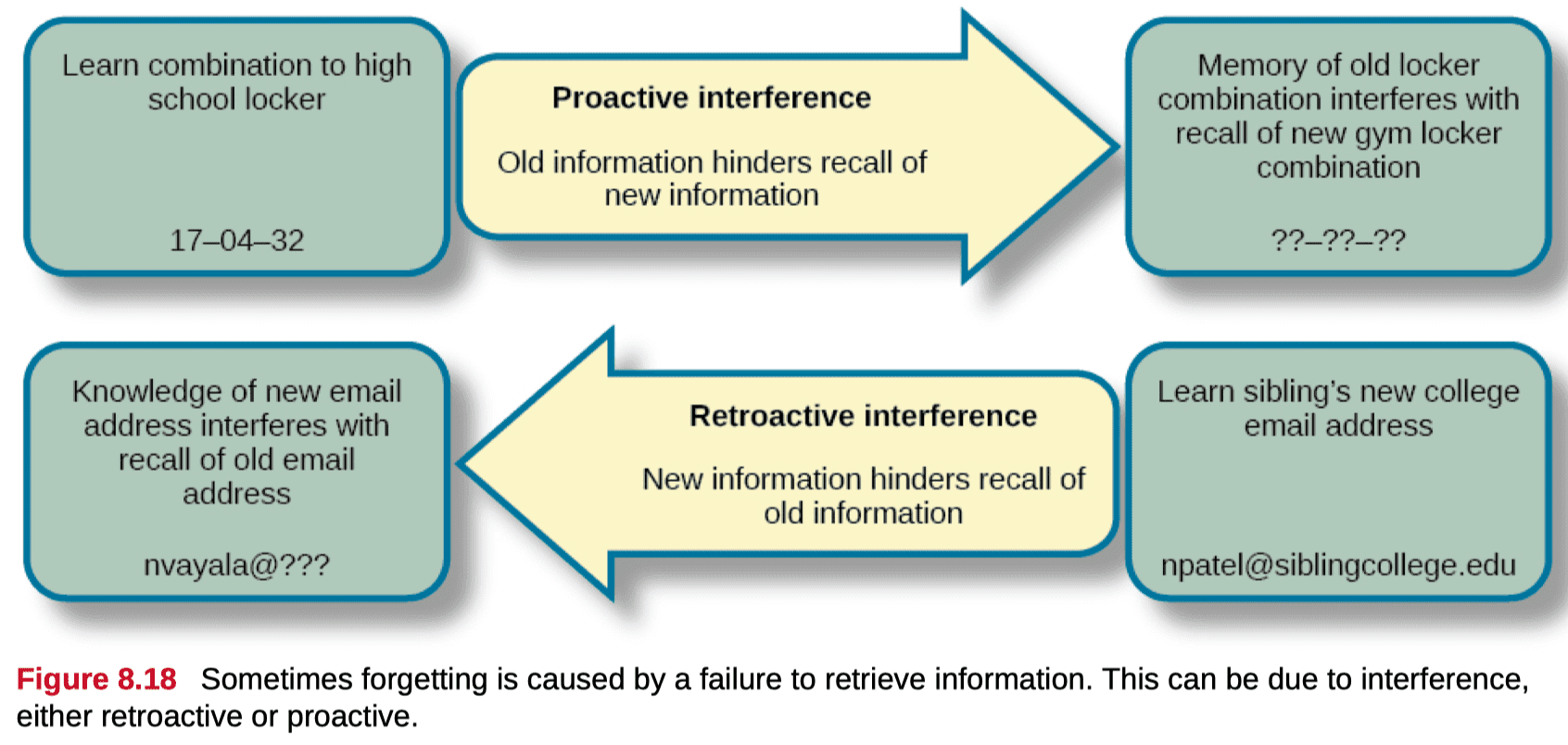
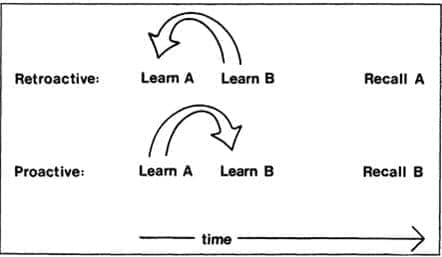
Question 32

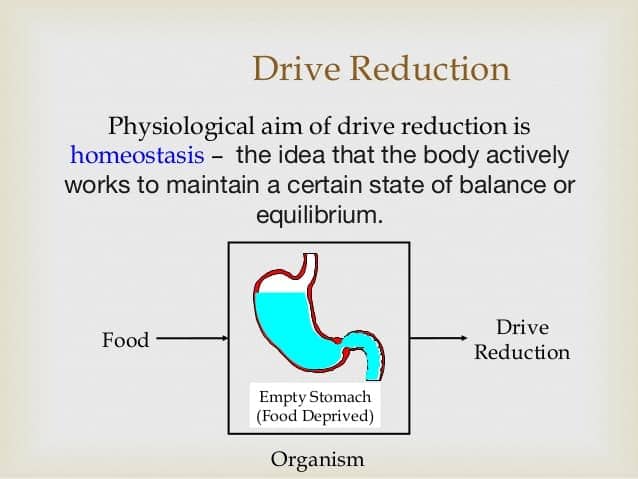
Question 34

- Stimulants are drugs that tend to increase overall levels of neural activity.
- A depressant is a drug that tends to suppress central nervous system activity.
- A hallucinogen is one of a class of drugs that results in profound alterations in sensory and perceptual experiences
Question 37

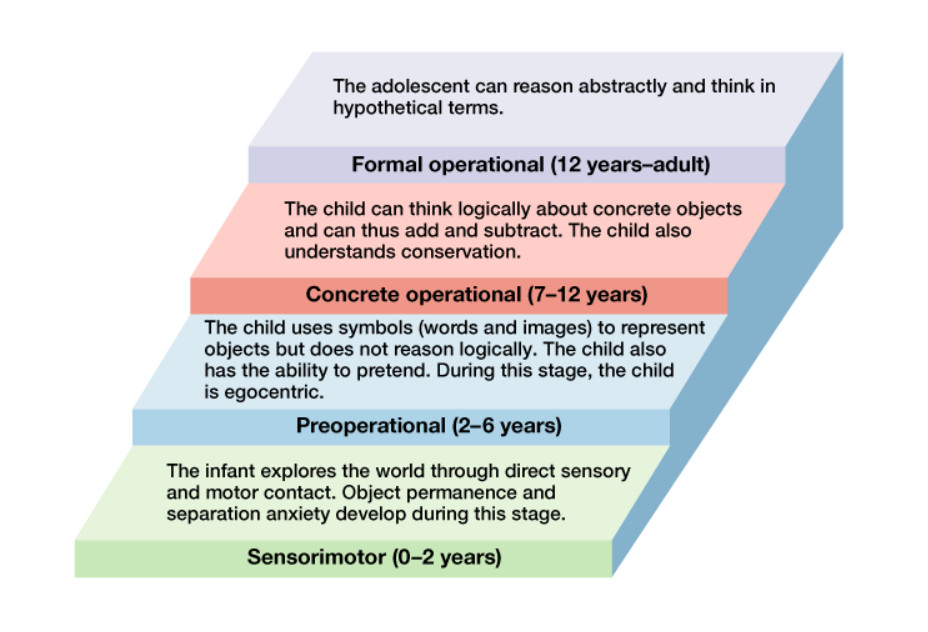
Question 39


Question 41

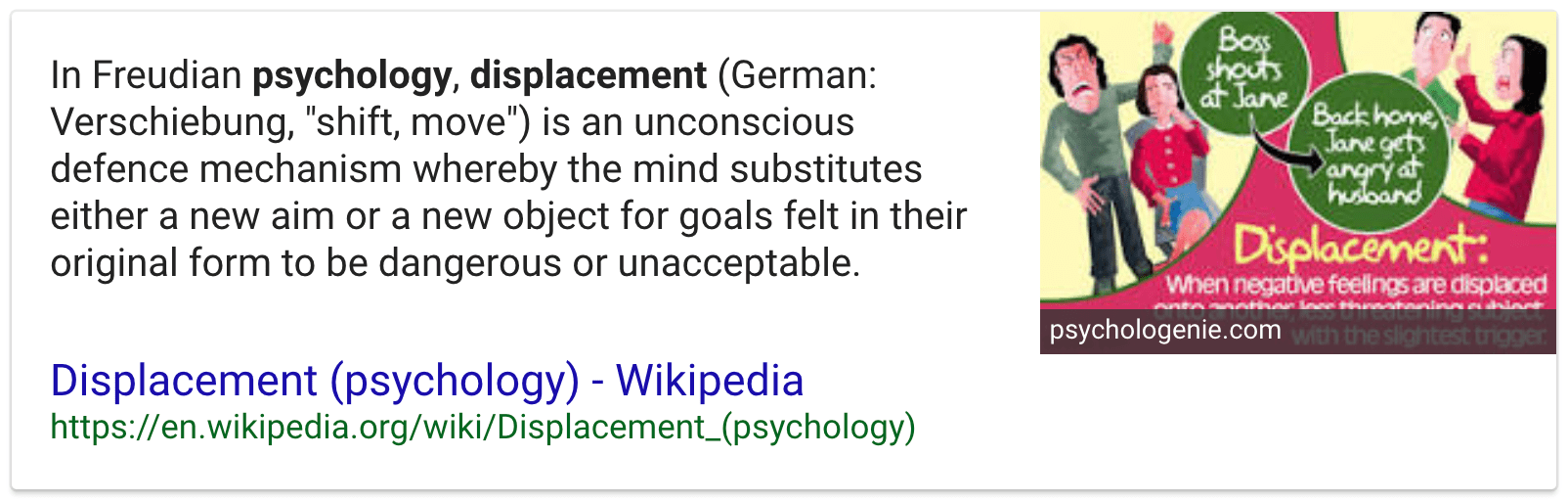
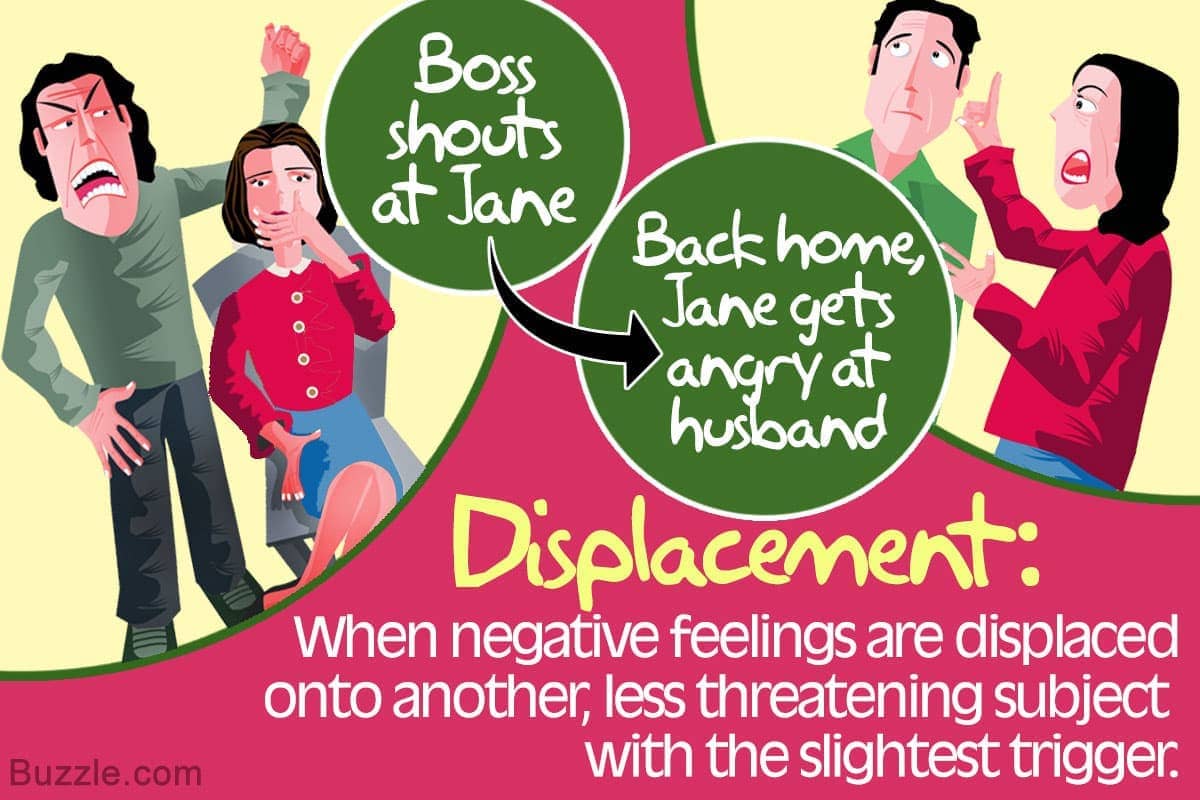
Question 45

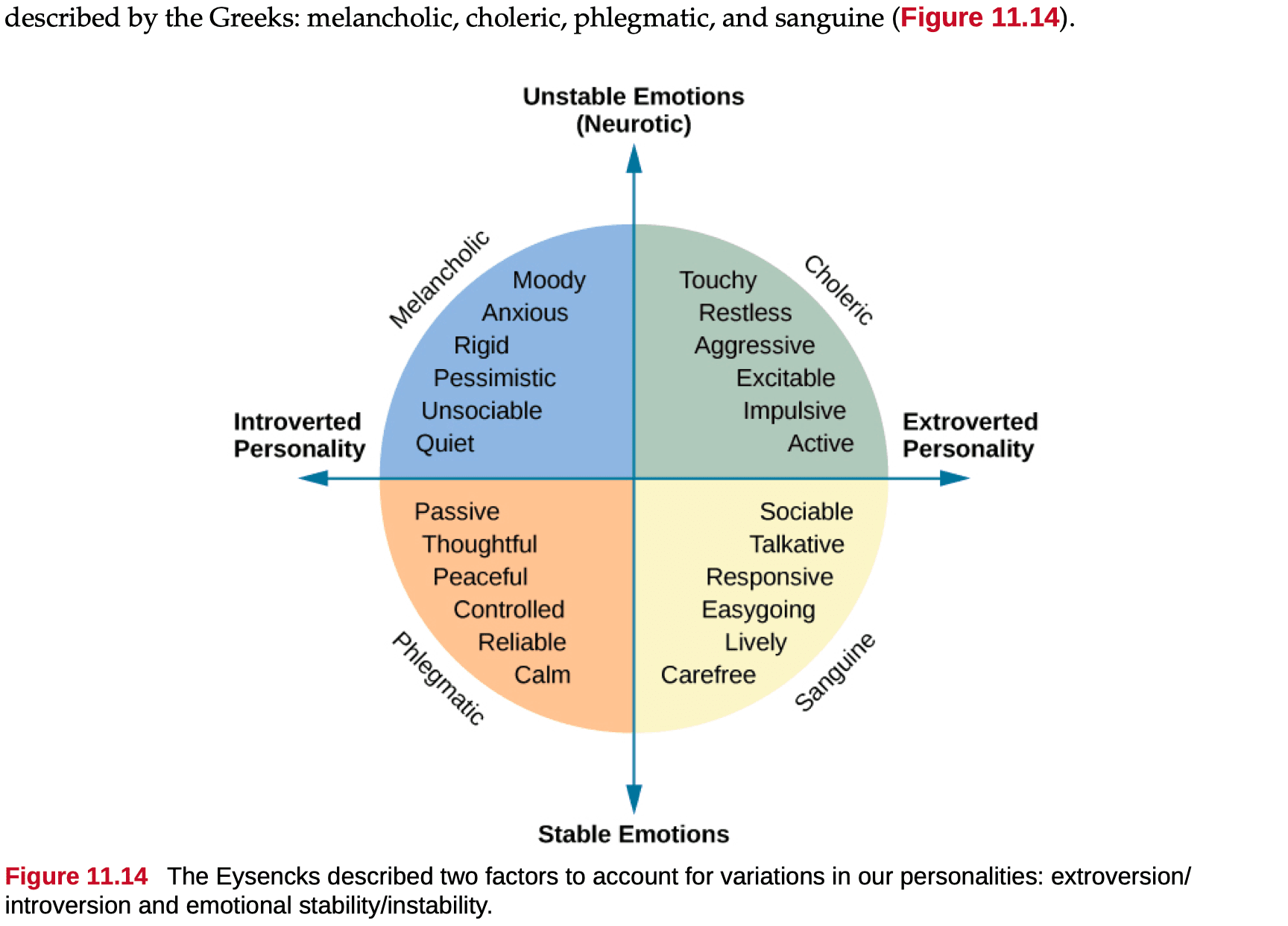
Question 47

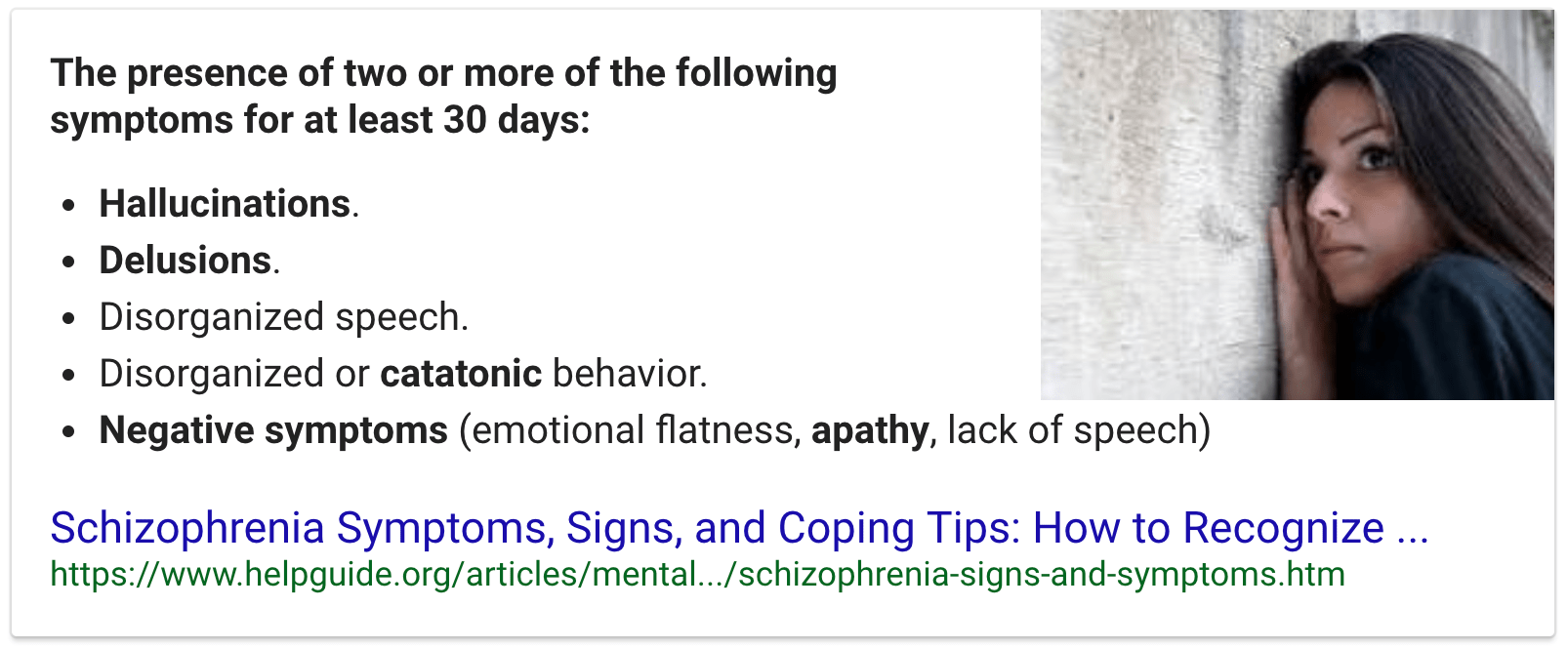
Question 50

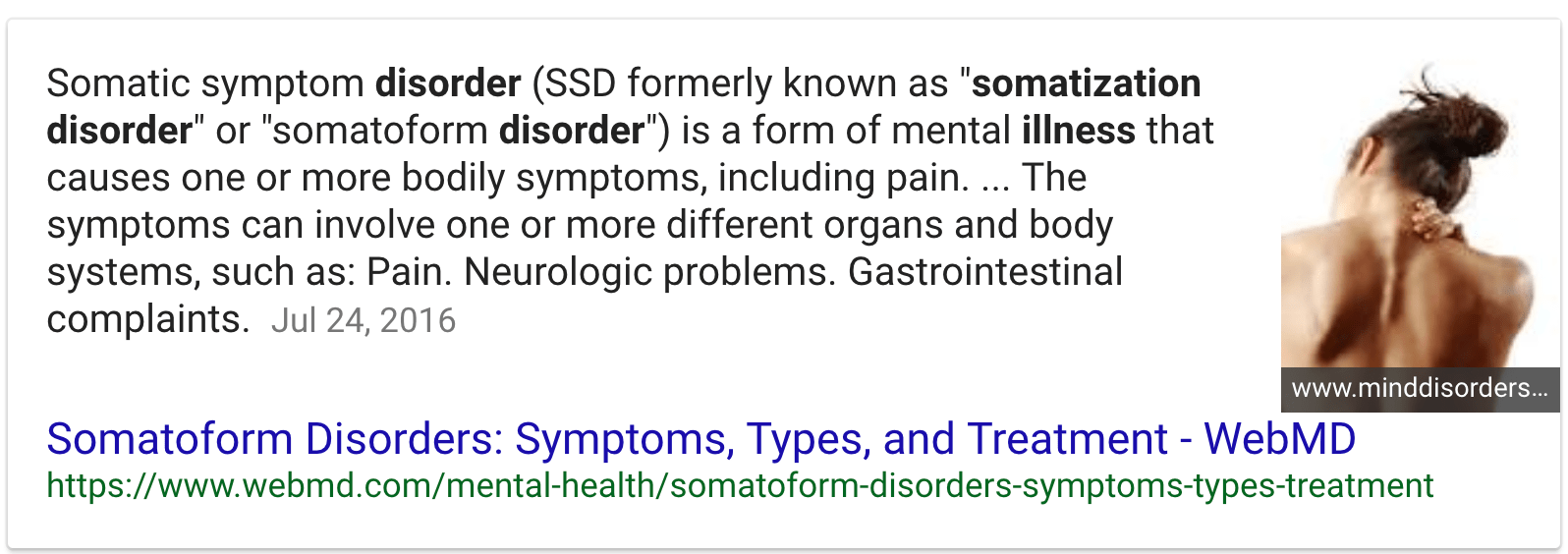
Question 56

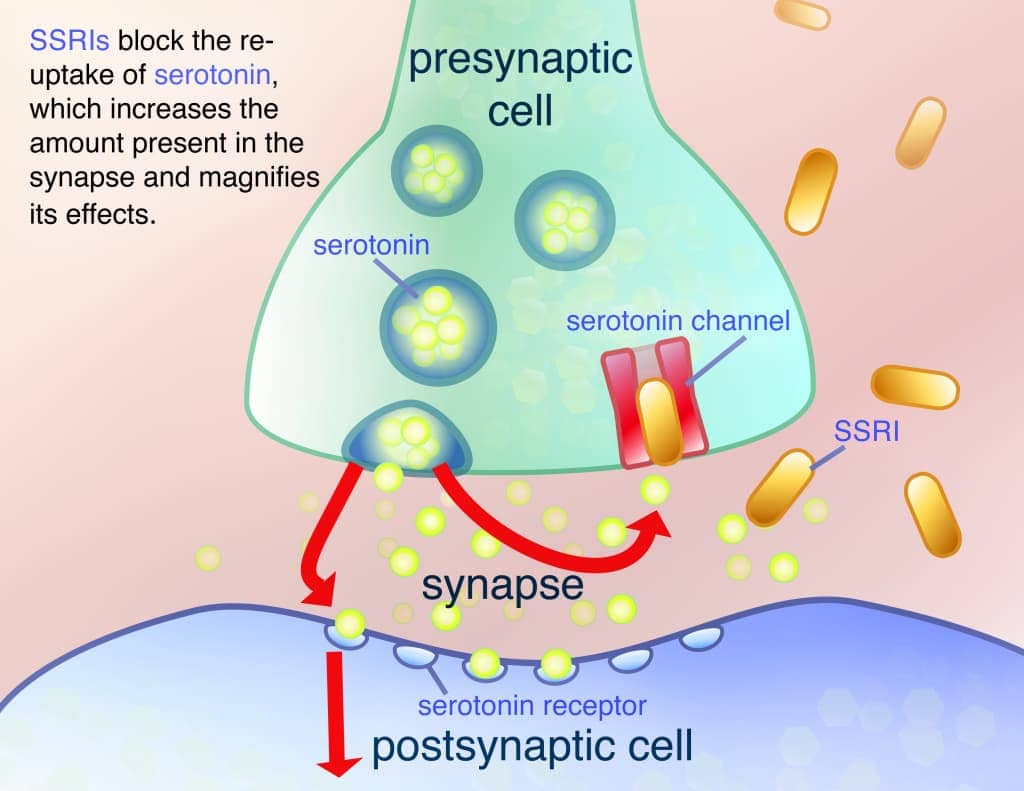
Question 57

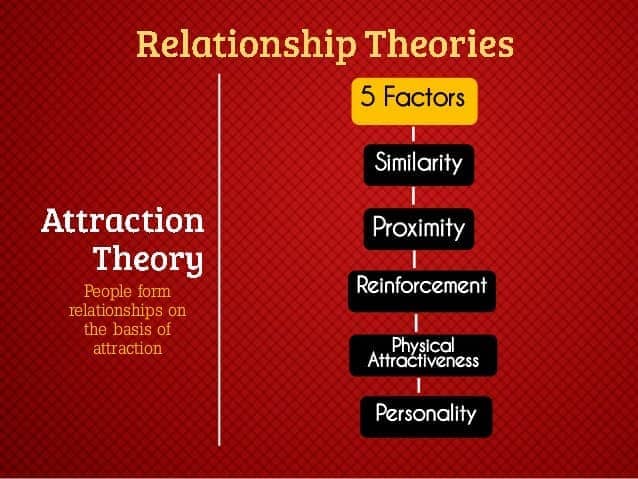
Question 58


Question 60

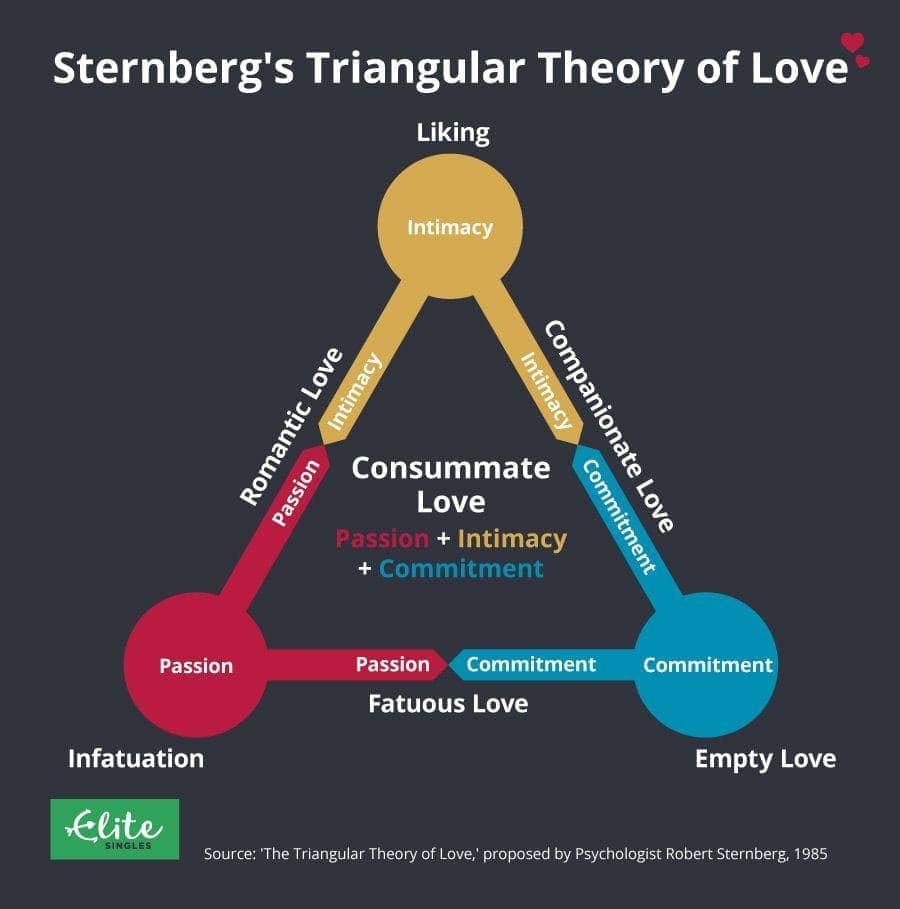
Question 61

Question 62

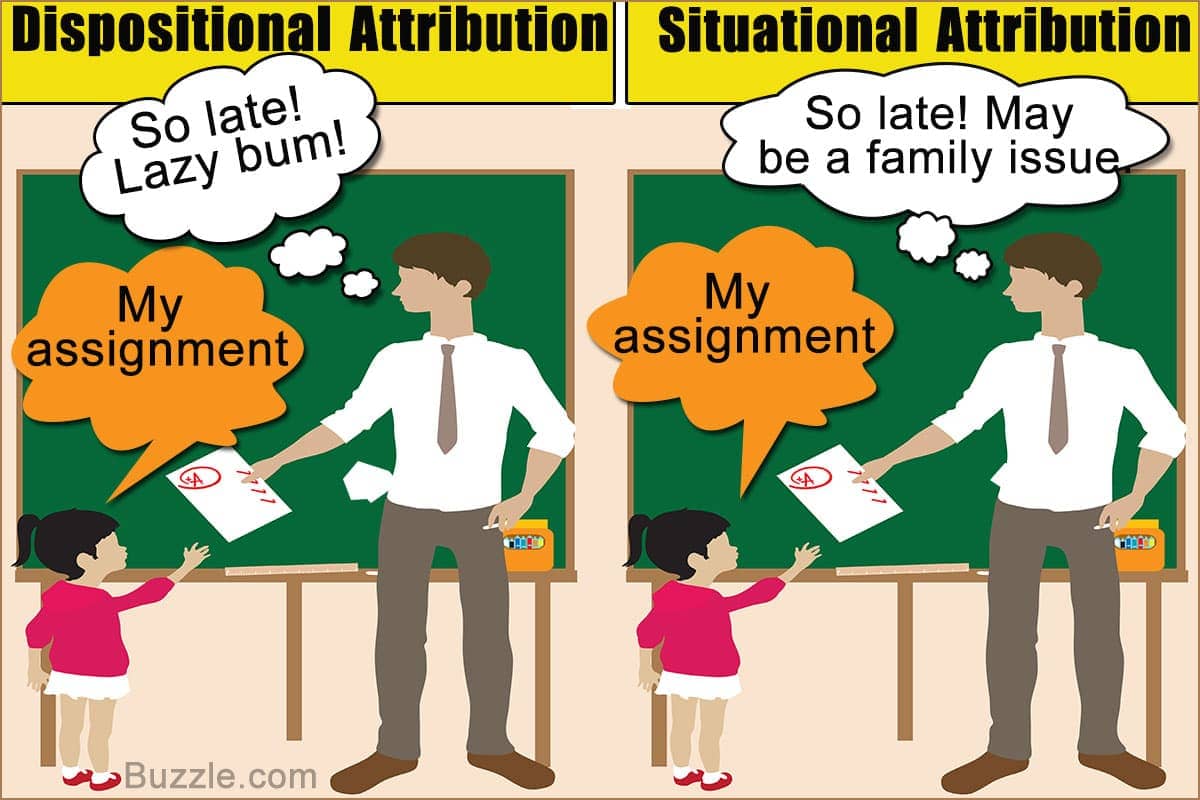
- dispositional: internal, personality, authoritarian personality
- situational: external, environment
Question 66

- Techniques Involving Radiation
- CT (Computerized Tomography): x-ray, tumor, significant brain atrophy, brain structure
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography): picture of active brain, show active and inactive areas of the brain
- Techniques Involving Magnetic Fields
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): generates a strong magnetic field
- fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging): shows changes in brain activity over time, more detailed images of the brain’s structure, better accuracy in time, than is possible in PET scans
- Techniques Involving Electrical Activity
- EEG (Electroencephalography): a measure of a brain’s electrical activity, array of electrodes, overall activity of a person’s brain,
Question 68

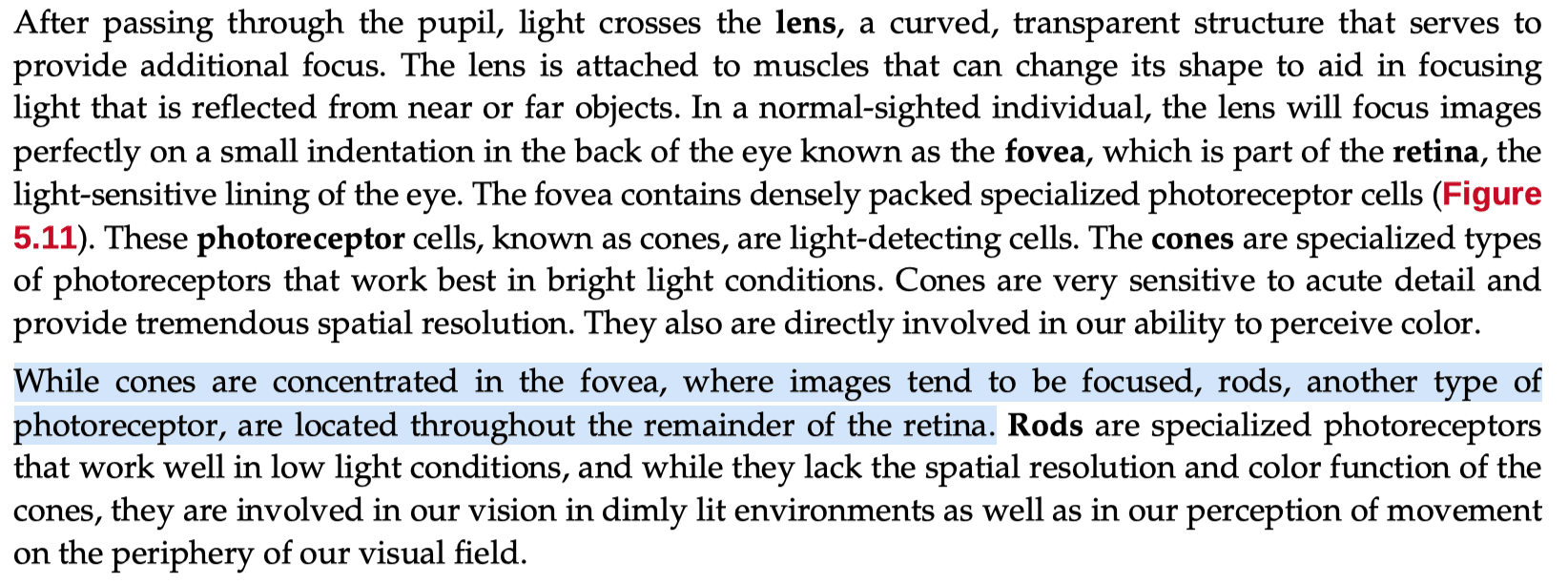

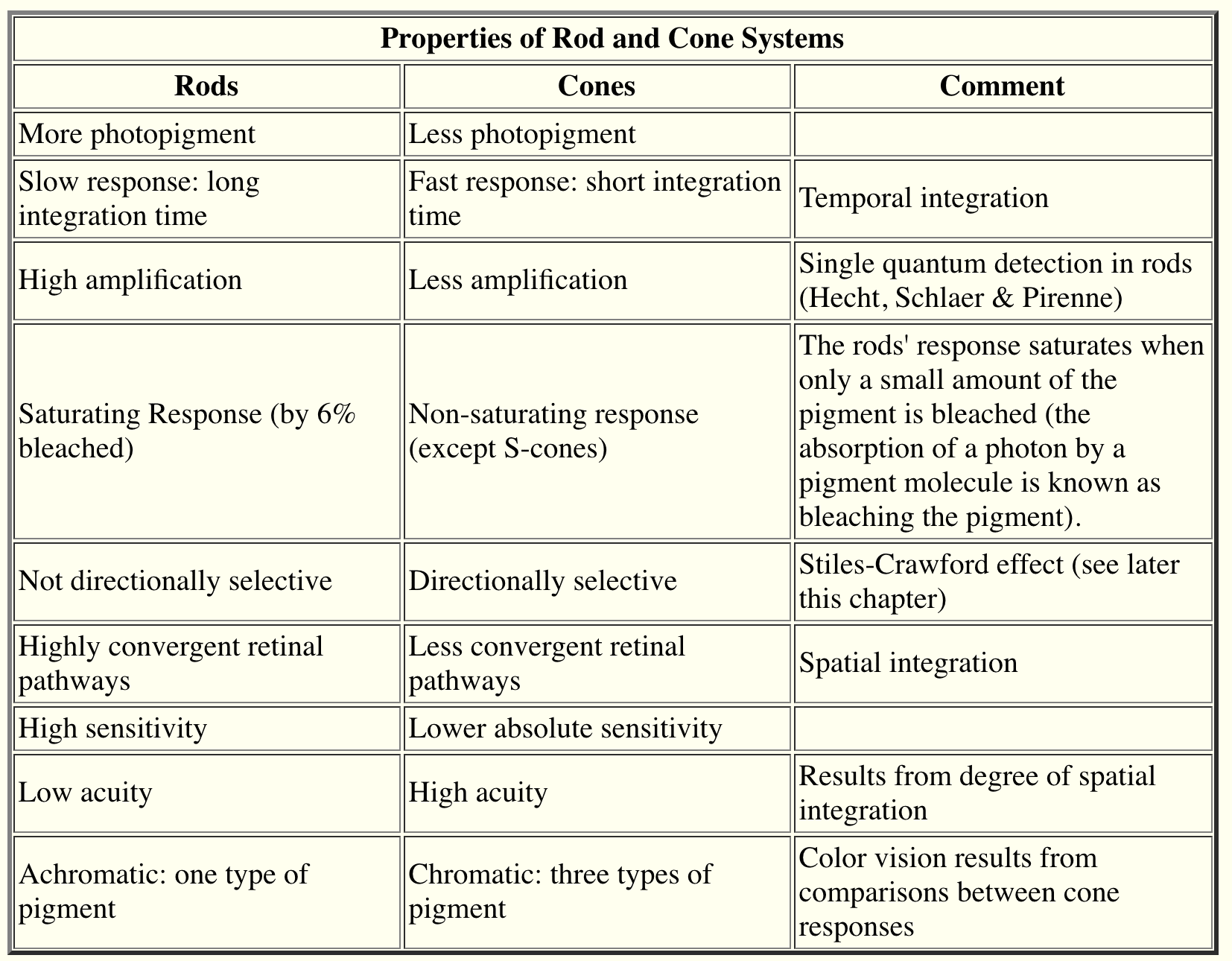
Question 71

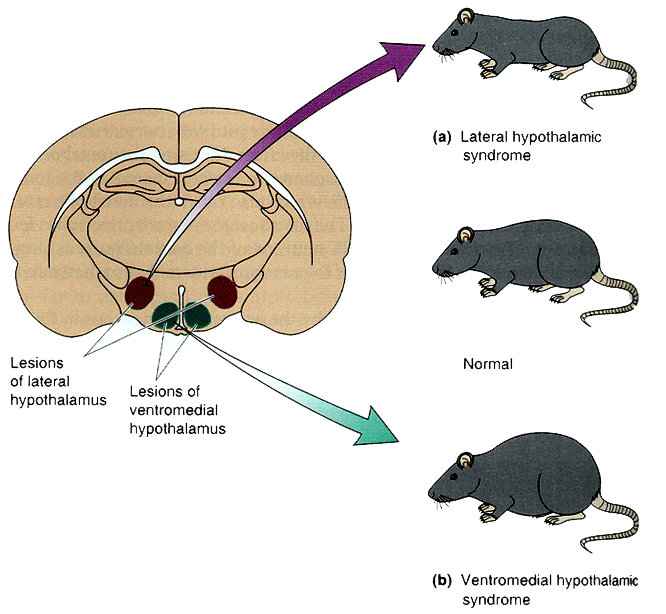
Question 72


Question 74

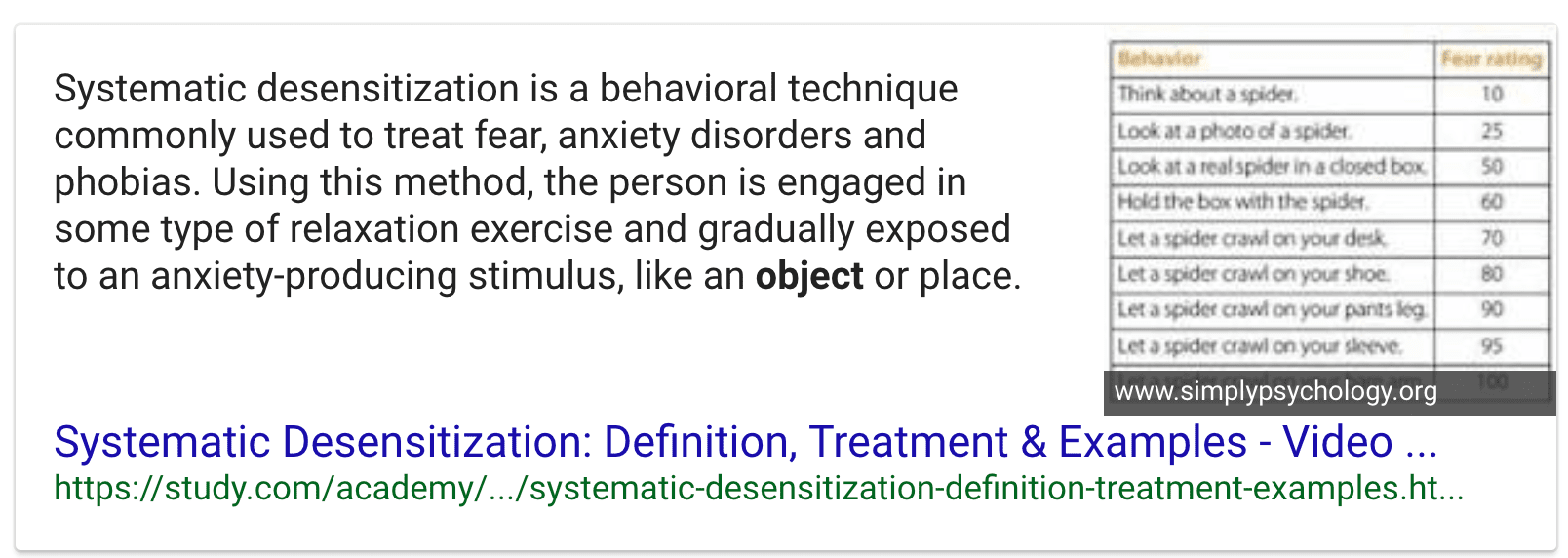
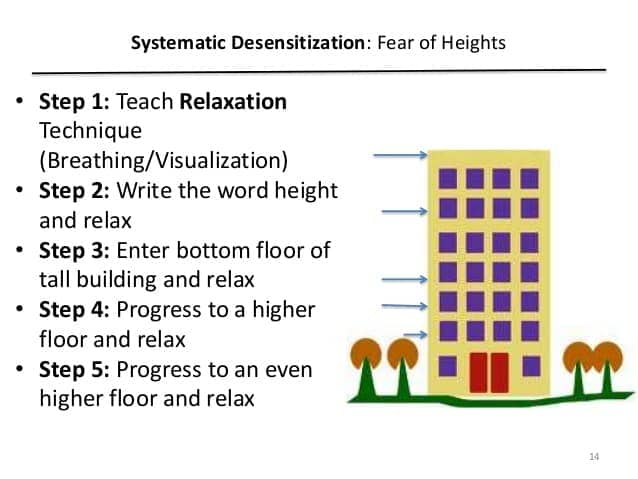
Question 76

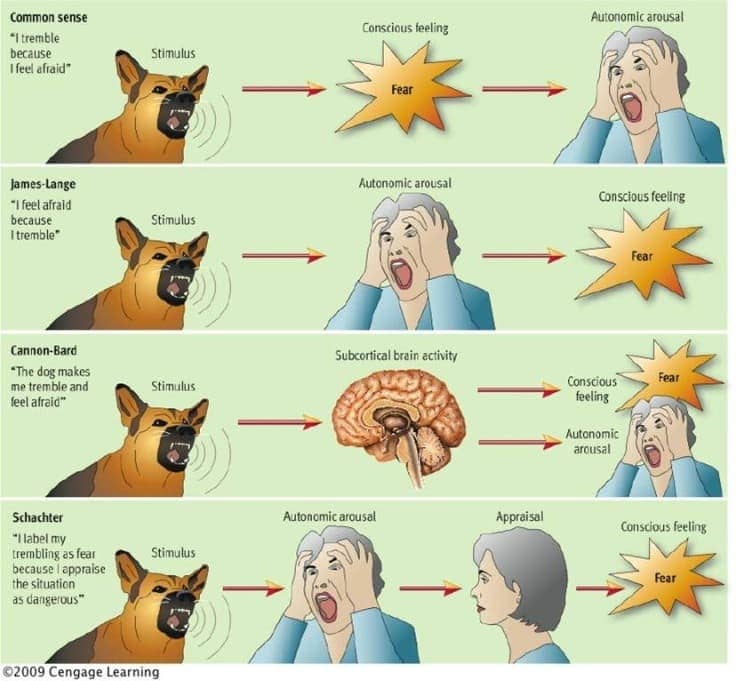
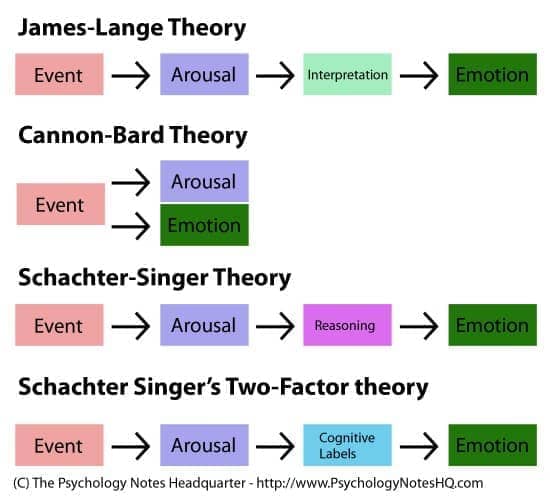
Question 77

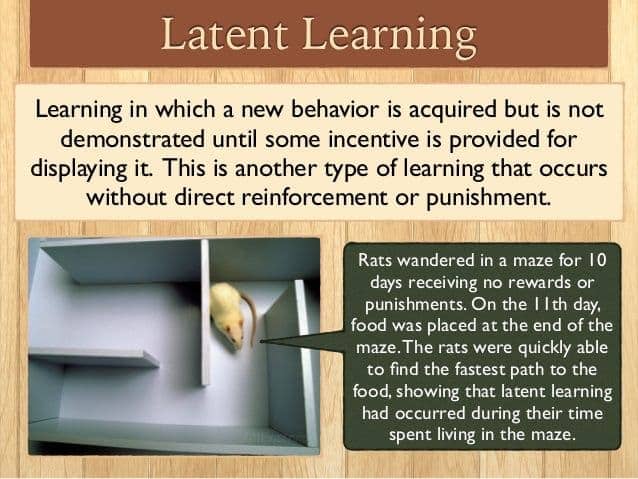
Question 79

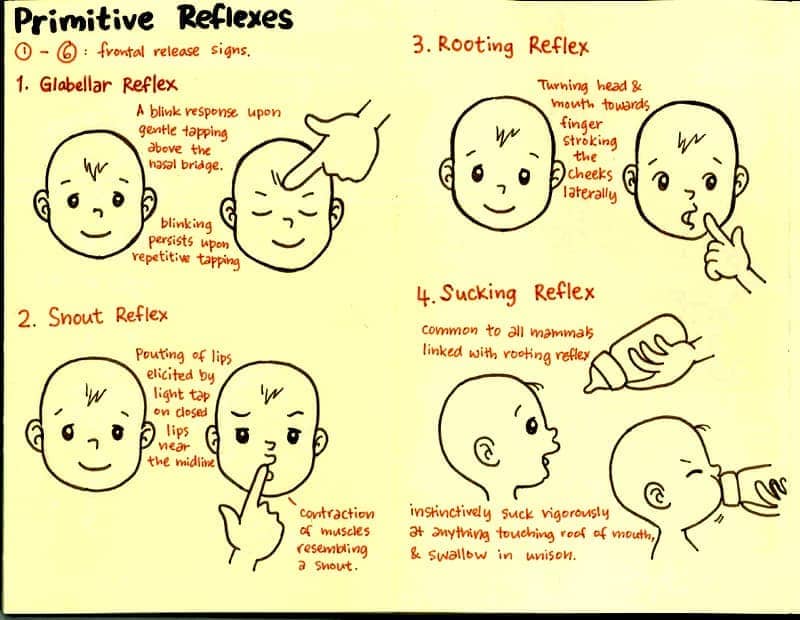
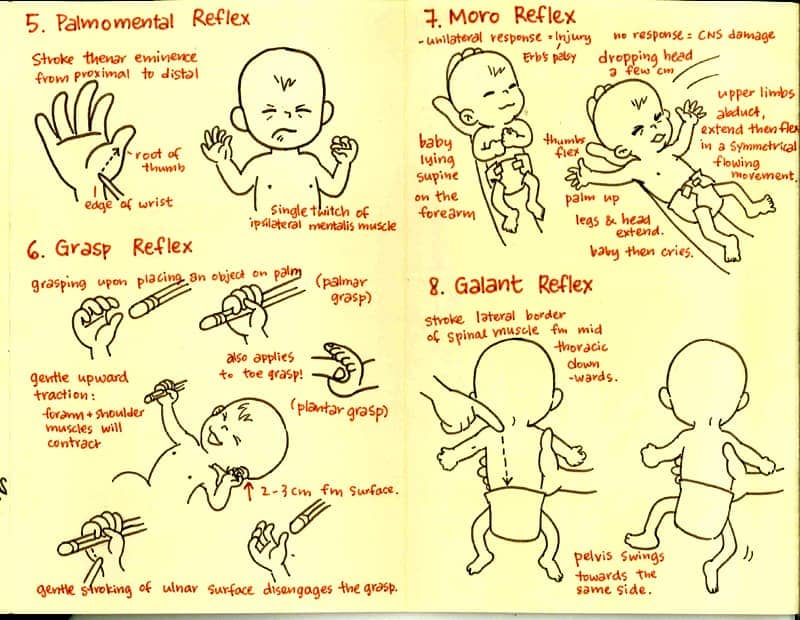
Question 80


Question 82


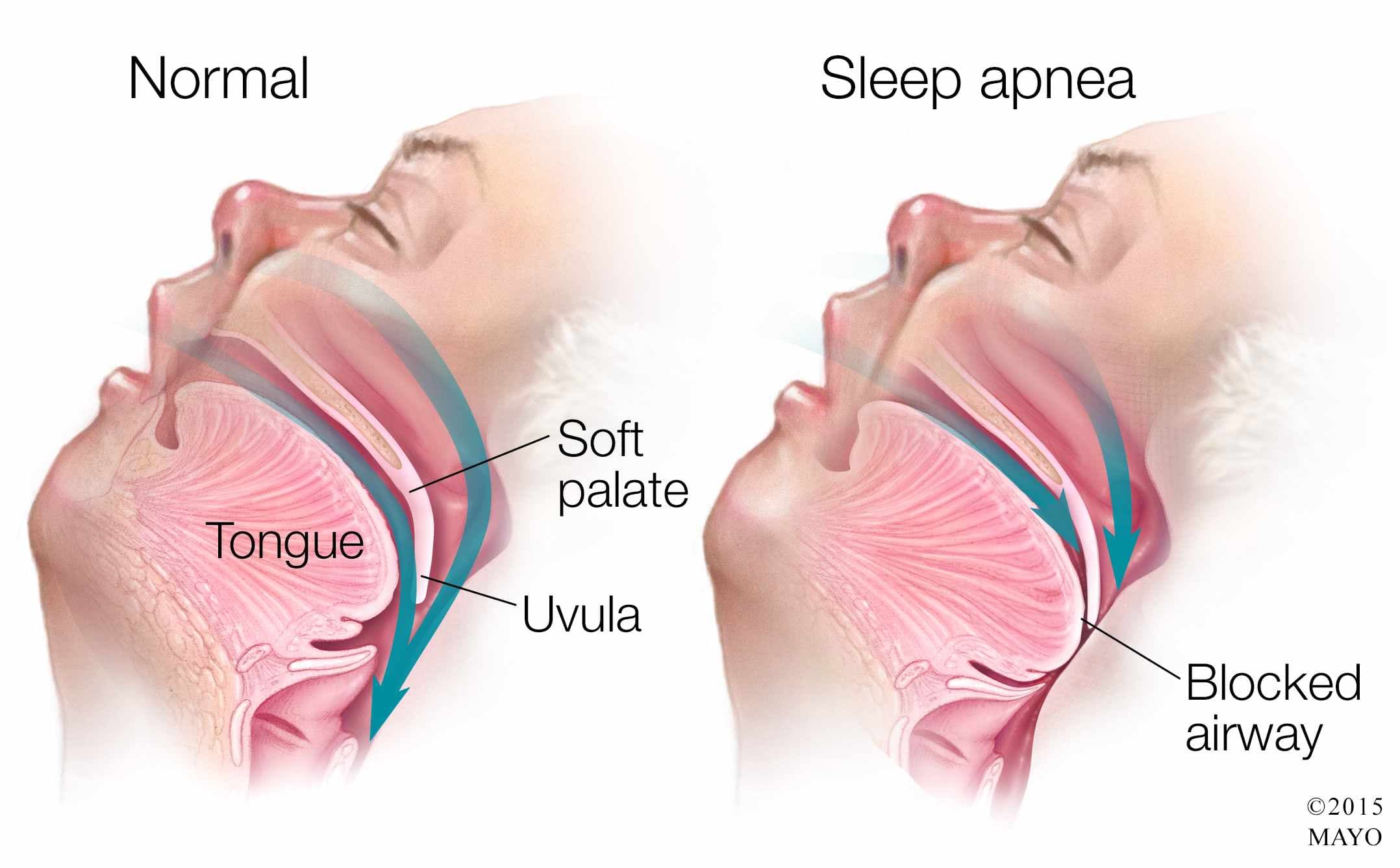
Question 84


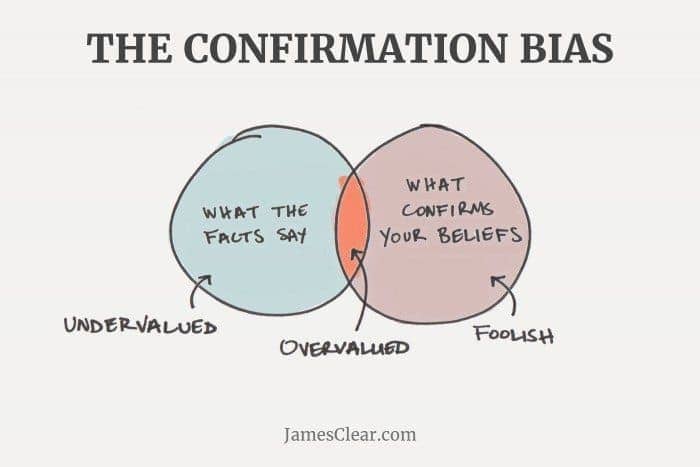
Question 86

Question 87

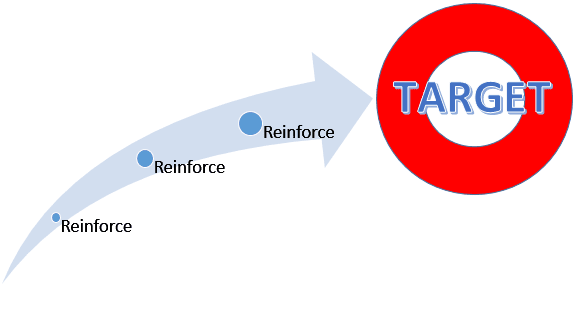
- Reinforce any response that resembles the desired behavior.
- Then reinforce the response that more closely resembles the desired behavior. You will no longer reinforce the previously reinforced response.
- Next, begin to reinforce the response that even more closely resembles the desired behavior.
- Continue to reinforce closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior.
- Finally, only reinforce the desired behavior.
Question 88




















































































![]()














